gingival thickness measurement|gingival tissue biotype : importing The objective to assess the accuracy of two different methods for gingival thickness measurement: the transgingival needle probing (TGNP) and the tension-free .
https://yariga.site/uploads/d1_2024-02-28-12.59.25.763-+0300_567.mp4 ڤیدیۆ: گۆڵی یەکەمی مانچێستەر یونایتد بەرامبەر نۆتینگهام فۆرێست 21كاتژمێر لهمهوبهر
{plog:ftitle_list}
Sensibilidade Free Fire: Redmi 9 Prime Nome da Sensibilidade: Geral: 70 Ponto Vermelho: 50 Mira 2x: 50 Mira 4x: 90 Mira AWM: 50 Olhadinha: 89 DPI Portanto, a .
This systematic review aimed to explore the diagnostic accuracy of two non-invasive methods (namely CBCT and ultrasound) for gingival thickness measurement at different tooth positions. Materials and methods
spring test github
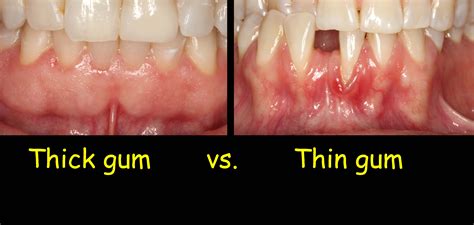
Various invasive and non-invasive methods were proposed to measure tissue thickness. These include direct measurement, probe transparency (TRAN) method, . Gingival thickness can be assessed by various invasive and non invasive methods. Thick and thin tissues often respond differently to inflammation and trauma. . Thin gingival biotype responds differently than thick gingival biotype. Gingival biotype assessment before various dental-related procedures is mandatory now to achieve a predictable and.
gingival tissue biotype
Gingival thickness was determined in 33 patients with plaque-induced gingivitis. Vestibular/buccal gingiva thickness was measured at the level of the gingival sulcus depth. . The objective to assess the accuracy of two different methods for gingival thickness measurement: the transgingival needle probing (TGNP) and the tension-free .
This study aimed to investigate the accuracy of gingival thickness measurement by two methods of clinical evaluation and intraoral ultrasonography. The gingival thickness was measured in the midbuccal area .Results: The mean gingival thickness ranged from 0.56 to 1.02 mm. Males had a significantly thicker gingiva as compared to females (P < 0.10). Significant differences were not observed . The aim was to retrieve the threshold of gingival thickness (GT), where the attribute of gingival translucency through probe visibility was altered. Methods In 200 patients, . Clinical photographs, sex, PV, probing depth, gingival width, papilla height, GT as measured with an ultrasonic device, and the ratio of crown width to crown length were .
gingival tissue
gingival thickness ultrasound
Download scientific diagram | Measurement of thickness of gingiva using an endodontic spreader from publication: Assessment of gingival thickness with regards to age, gender and arch location .
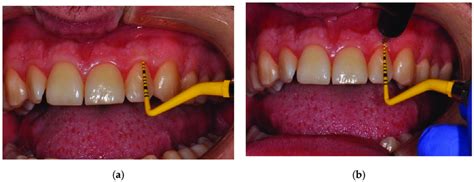
The ultrasonic device Pirop G® with a frequency of 20 MHz and CBCT/CAD/PDIP were used to measure gingival thickness at upper canines and incisors in three points localized midbuccally, namely .
In a study performed by Kloukos et al. in 2018, it was reported that ultrasonographic measurement of gingival thickness yields results statistically similar to those using transgingival probing, although ultrasonographic measurements were slightly higher . Meanwhile, we observed that the mean values for ultrasonographic evaluation were .
for gingival thickness measurements. For both (ES and SC) groups, facial gingival thickness (FGT) and lingual gingival thickness (LGT) measurements were assessed at 1 mm apical tothezenithofthemid-facialandmid-lingualgingivalmargin at an angle perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth. In the ES group, the operator inserted a standard no. 35 end- Objectives The present study was performed to determine the gingival dimensions (width and thickness) among young individuals in a central Indian population. Materials and methods Periodontal probing depth, width of the keratinized and attached gingiva, and gingival thickness were recorded on maxillary and mandibular teeth from central incisor . This study aimed to investigate the accuracy of gingival thickness measurement by two methods of clinical evaluation and intraoral ultrasonography. The gingival thickness was measured in the .Background: The measurement of the thickness of the gingival tissues has been done using different techniques. Trans-gingival probing with a graduated probe, use of vernier calipers, ultrasonography and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT), have all been tried, but no one technique has been shown to be consistent and better than the others.
Results. The mean gingiva thickness was 0.72 mm measured on MRI and 0.97 mm measured on CBCT, with a mean difference between the measurement methods of 0.17 ± 0.27 mm (p < 0.001).Measurement agreement between the index tests (MRI and CBCT) and the clinical reference standard (probing) yielded an overall percent agreement of 64.94% and .Measurements for free gingival thickness (GT1), cementoenamel junction gingival thickness (GT2), supracrestal gingival thickness (GT3), subcrestal 1 mm gingival thickness (GT4) and BT at 1, 3 mm .
Objective This diagnostic accuracy study aims to present the first measurements of gingiva thickness around lower anterior teeth using dental magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and to compare these measurements with two established methods: (1) gingival phenotype assessment via periodontal probing, and (2) the superimposition of cone-beam computed . The obtained results in %R&R prove the good recognition of methodology as well as the usefulness of the device in measuring gingival thickness (GT) in the mucogingival complex. BACKGROUND Successful periodontal and implant surgery as well as orthodontic treatment often depends on gingival and mucosal thickness. So far there has been no generally .
However, clinically, measuring gingival thickness with accuracy and cost-effectiveness can be done using an endodontic spreader under adequate local anesthesia. CONCLUSION. It has been demonstrated that the thickness of the gingiva reduces with increasing age in both maxillary and mandibular dental arches. However, more thickened gingiva was . This study was undertaken to explore the periodontal biotype distribution in a young Chinese population and to evaluate the accuracy of different methods for gingival thickness (GT) measurement. Digital measurement of gingival thickness is comparable with direct clinical assessments performed with transgingival horizontal probing using an endodontic spreader. Digital assessment of gingival thickness is a non-tissue invasive, reliable, and reproducible method that could be utilized as an alternative to horizontal transgingival probing.
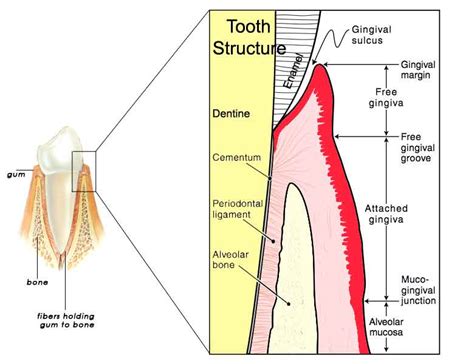
depth of the gingival sulcus and midway between the sulcus depth and mucogingival line. • Free gingival thickness averaged 1.56 mm + 0.39, attached gingival thickness averaged 1.25 mm + 0.42 and the total mean thickness for all areas measured was 1.41 mm. • Thickness in mandibular free and attached gingival and maxillary free
gingival thickness
The measurement of the thickness of the soft tissues was done 2mm apical from the gingival margin of the anterior and premolar dental units, associated with the thickness of the buccal bone table .Objectives: This study was aimed at evaluating the correlation and reproducibility of gingival thickness quantification using digital and direct clinical assessment methods. Materials and methods: Patients in need of tooth extraction were allocated into two groups according to the gingival thickness measurement method, either using an endodontic spreader (pre .In this method, the probing limit to measure the gingival thickness was defined at 2 mm and it was implemented in the middle of the buccal surface of the upper anterior teeth. As a result, they concluded that, when the thickness of the gingiva was less than 0.6 mm, the gingival phenotype was suggested in all cases thin and, when the thickness . To overcome these drawbacks, Januario et al. 14 proposed a non-invasive technique called soft tissue cone beam computed tomography (ST-CBCT) to visualize and measure the gingival thickness non-invasively on CBCT images. CBCT imaging is part of the preoperative assessment in implant surgery; thus, ST-CBCT offers a simple method for the .
Cone-beam computed tomography images and the probe transparency method with color-coded probes are reliable for identifying the gingival phenotype in the maxillary anterior region, based on comparisons to direct transgingival probing. Gingival phenotype is closely related to treatment success and aesthetic results in the maxillary anterior region. Several .
Objective: To measure the thickness of five different brands of gingival retraction cords and verify whether there would be a relationship among the sizes and their numbers and a coherent . The measurement of the thickness of the gingival tissues has been done using different techniques. Trans-gingival probing with a graduated probe, use of vernier calipers, ultrasonography and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT), have all been tried, but no one technique has been shown to be consistent and better than the others. . The buccal gingival thickness measurement points were established under magnification for enhanced visualization. The same linear measurement tool used for assessing buccal gingival thickness was employed to locate the 2 measurement points, starting from the uppermost point of the buccal gingival tissue and extending vertically downward by 1 .
The objectives of the present study were (I) to determine the validity and reliability of measuring gingival thickness (GTH) with a recently developed, commercially available ultrasonic device; (II) to measure GTH in relation to tooth type and age of proband; (III) to correlate GTH with varying forms of premolars, canines and incisors. A method was established for measuring gingival thickness based on cone-beam computed tomography. The gingival biotypes had a positive correlation with gingival thickness of the CEJ.54 Braz Dent Sci 2015 Apr/Jun;18(2) Gingival retraction thickness measurement and comparison of different cords Massari C et al. Graph 1 - Mean values (mm) of the thickness of different cords regarding the same size assigned by the manufacturers.The horizontal lines represent the cords without significant thickness difference.Results: No signicant relationship between papilla ll, height, width and gingival probe transparency or gingival thickness was found. Gingival thickness and gingival probe transparency showed a signicant relationship (P < 0.001). There was a signicant relationship between papilla height and papilla ll (P = 0.028). A papilla which lled the inter -
gingival morphology
webRestricted Content: Sign in to view! 18+ Restricted Content: Sign in to view!
gingival thickness measurement|gingival tissue biotype